General description of Spool2XML
The normal printing process on the IBM i platform works like this:

The printing program use a printer file to print the final spooled file. The use of an external printer file is a prerequisite for Spool2XML.
When introducing Spool2XML the new process looks like this:

A short introduction to the individual parts:
The new Spool2XML printer file
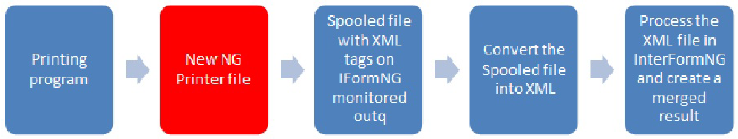
A new printer file is needed to ‘fool’ the program into creating a different spooled file. This is created by the command: IFORMNG2/CVTPRTFXML. In the XML definition you define the
output queue in which the final, merged spooled file will be generated, and if it should be broken up into smaller print outs. The new printer file can be placed higher in the library list or it
can replace the previous printer file. It is recommended to create the new printer file in another library.
The new XML Spooled file

The XML spooled file contains the XML structure as it should be in the XML file. The XML data in the spooled file is written with a start and end tag for the record format printed and fields defined in the record format is written within start and end tags within this record format. So the XML structure is valid, but not structured in a heirarchy apart from this.
The output queue of the printer file must be one of the output queues, that is monitored by Spool2XML for automatic processing.
Convert the spooled file into XML
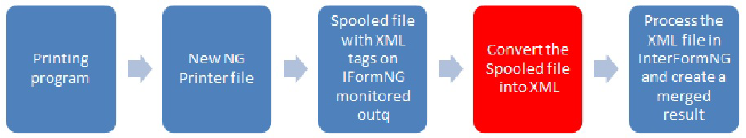
The XML definition sets the structure of the final XML (what format is a sub-format to another - or in XML: Which formats are considered as subtrees to other formats?). It also sets the level
breaks to determine e.g. when a new XML files should be created (as one spooled file can be split up into many XML files).
Process the XML file in InterformNG2
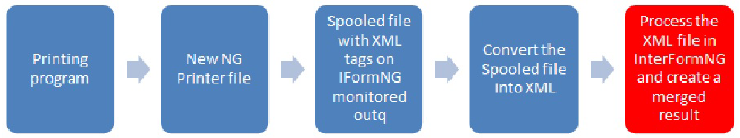
The final step is to let InterformNG merge the XML file with a template (selected in the XML definition) and create a new merged spooled file, a PDF, an email or whatever output you want.
Related Articles
XML
XML is used widely in InterformNG2 as both input and output payload in the workflow (and of course in the designer). Please notice, that some workflow components are listed as accepting only XML as input, where they actually also accept an IBM i ...Split spool (complex key)
A spooled file can be split into smaller files depending on the contents e.g. to split up a larger spooled file with many invoices into individual invoices. If the other spooled file split functions are not enough, then you can consider this workflow ...PDF Metadata to XML
The advanced, utilities workflow component, PDF Metadata to XML can help you to extract both metadata as well as key/values for form fields from a PDF file. The PDF must be loaded into the payload of the workflow before running this component. The ...XML to CSV
If you want to output CSV files from InterformNG2, then there are three options: You can use an Excel template and then use the workflow component, Excel template to CSV followed by e.g. To filesystem to save the output as a CSV file. For this you ...Rule-based XML validation
This advanced validation workflow component, Rule-based XML validation, can validate XML according to rules. The rules for rule-based validation can be used to validate documents in XML format. A suggestion for implementation can be found here. The ...